Our work on the effects of 'deltaG' ketone supplementation in muscle and heart
31 Jan 2022
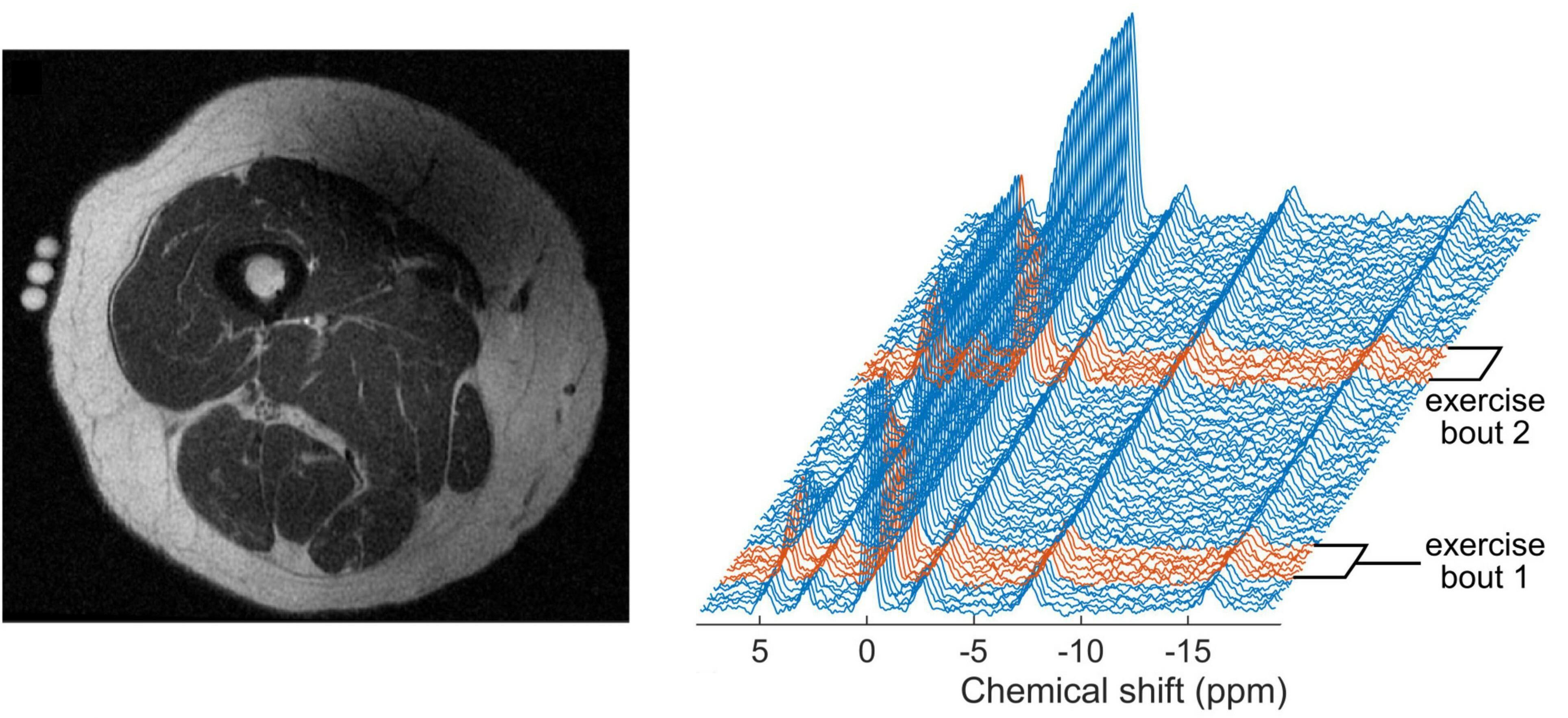
Our new article, titled Evaluation of Acute Supplementation With the Ketone Ester deltaG in Healthy Volunteers by Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle 31P Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, has just been published in Frontiers in Physiology as part of the Research Topic “New Views on Old Molecules: MR Spectroscopic Techniques & Insights on Physiology”. Here’s a brief synopsis of the research:
In this acute intervention study, we investigated the potential benefit of ketone supplementation in humans by studying cardiac PCr to ATP ratios and skeletal muscle PCr recovery using 31P-MRS before and after ingestion of a ketone ester drink. We recruited 28 healthy adults: 12 age 23–70 for cardiac 31P-MRS, and 16 age 60–75 for muscle 31P-MRS. Baseline and post-intervention 31P-MRS scans were performed in one visit, where 25 g of the ketone monoester, deltaG®, was administered after the baseline scan. Post-intervention 31P-MRS was timed 30 min after deltaG® ingestion. In blood samples, post-intervention glucose, lactate and non-esterified fatty acids decreased (−28.8%, −28.2%, and −49.1%, respectively), while ketone body D-beta-hydroxybutyrate increased from mean (SD) 0.7 (0.3) to 4.0 (1.1) mmol/L. Cardiac PCr/ATP and muscle metabolic parameters did not change. Acute ketone supplementation caused mild ketosis in blood, with drops in glucose, lactate, and free fatty acids; however, these changes were not associated with 31P-MRS measures in heart or muscle. Future work may investigate longer-term ketone supplementation on tissue energetics in groups with compromised mitochondrial function.

